-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 32
Description
Summary
I discovered a cryptographic vulnerability in the implementation of the Shamir Secret Sharing scheme. The implementation explicitly forbids polynomial coefficients from colliding with the secret byte or with each other. This rejection sampling introduces a statistical bias that violates the Information-Theoretic Security property of Shamir's scheme. It allows an attacker with
Introduction
In a standard Shamir Secret Sharing Scheme over
For the scheme to maintain perfect secrecy, the coefficients
The current implementation forces coefficients to be distinct from the secret and distinct from each other.
Code snippet:
for (let b = 0; b < secret.length; b++) {
let q = [secret[b]];
for (let i = 0; i < threshold - 1; i++) {
do {
// ... entropy generation ...
w = e[ePointer++];
} while (q.includes(w)); // <--- VULNERABILITY
q.push(w);
}
// ...By using while (q.includes(w)), the code enforces that pybtc) implementation, creating a cross-library inconsistency and a security flaw in the JS version.
Attack (Entropy Reduction)
An attacker possessing
- Iterate through all 256 possible candidates for the Secret Byte (
$S_{guess}$ ). - Using Lagrange interpolation (or system of linear equations), derive the implied coefficients
$a_1, \dots, a_{t-1}$ that would result in the held shares if$S_{guess}$ were the true secret. - Check the constraint: If any derived
$a_i == S_{guess}$ or$a_i == a_j$ , then$S_{guess}$ is impossible under this specific implementation. - Eliminate
$S_{guess}$ from the search space.
In a correct implementation, every
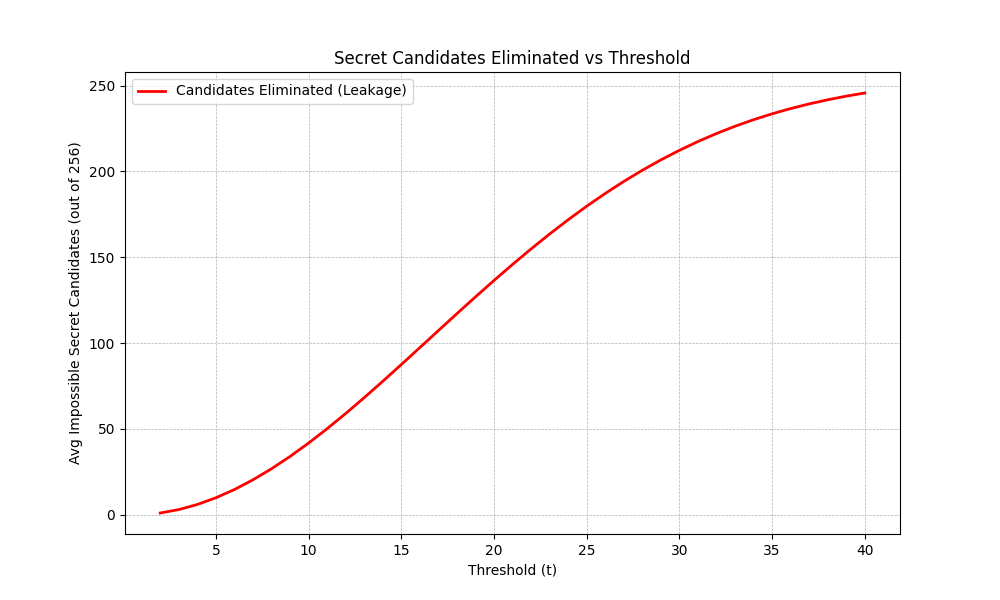
Statistical Impact
The probability that a random polynomial violates this constraint increases significantly as the threshold
For a small threshold (e.g., 3), the leakage is small. However, as
Here is a Python simulation that proves the reduction in search space
And here is a chart that shows how security degrades as the threshold increases:
Recommendation
Remove the check while (q.includes(w)). The coefficients should be allowed to collide with the secret and with each other to ensure uniform distribution over the finite field. The Python implementation is correct and does not include this check.